Fracking: Blessing or Curse?
Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, has become a lightning rod for controversy in the energy industry. This article explores the potential benefits and risks associated with this contentious practice, particularly its impact on groundwater and local environments.
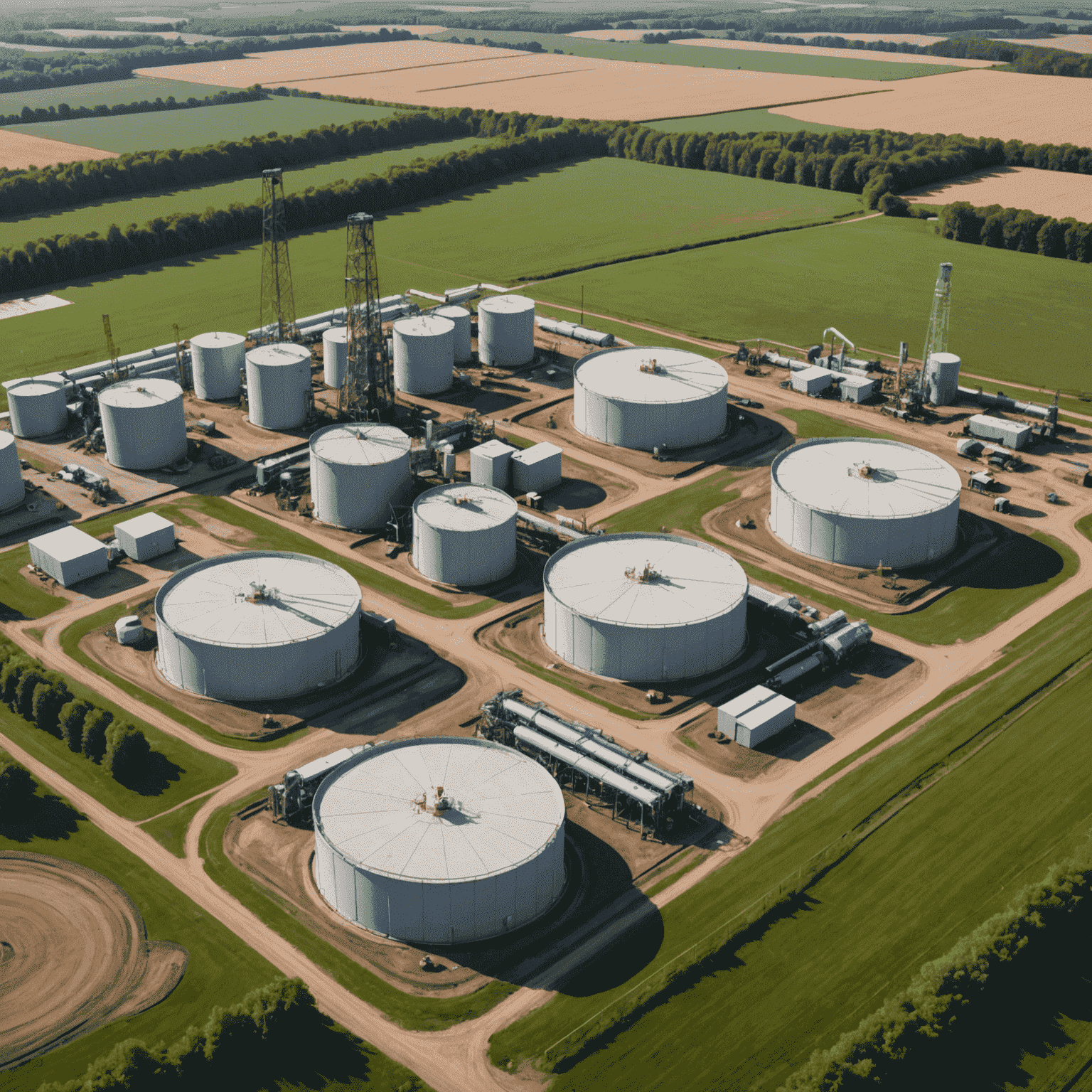

The Promise of Energy Independence
Proponents of fracking argue that it offers a path to energy sustainability and reduced carbon emissions compared to coal. The technique has unlocked vast reserves of natural gas, potentially providing a bridge to renewable energy sources. However, this promise comes with significant environmental challenges.
Groundwater Contamination Concerns
One of the primary environmental impacts of fracking is the potential for groundwater contamination. The process involves injecting a high-pressure mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into deep rock formations. Critics argue that this can lead to:
- Methane leakage into aquifers
- Chemical contamination of drinking water sources
- Increased seismic activity in fracking areas
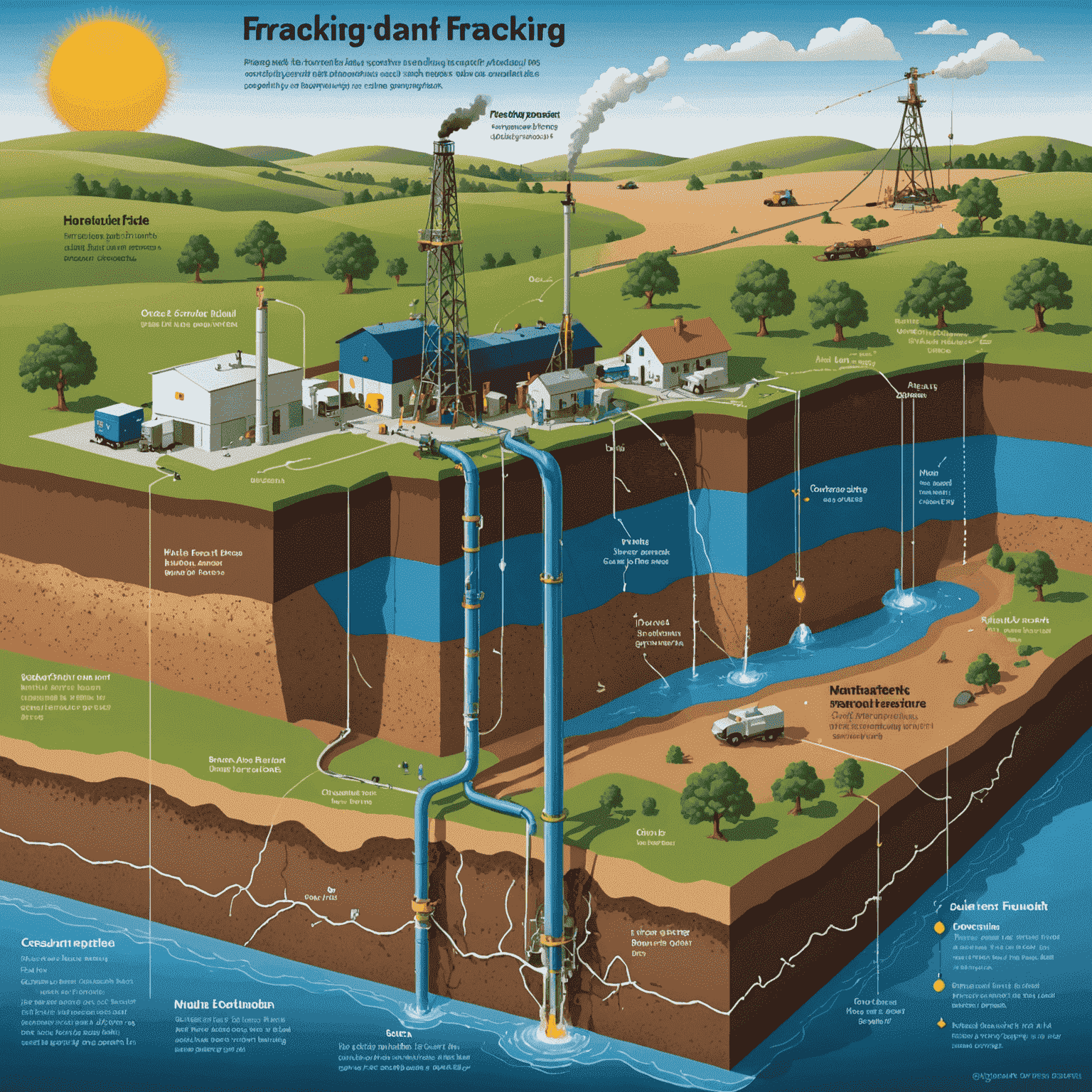
Ecosystem Disruption
Beyond water concerns, fracking operations can lead to significant ecosystem protection challenges. The industrial waste generated, potential oil spill effects, and the overall environmental impact on local flora and fauna are substantial. Fracking sites often require:
- Large-scale land clearing
- Construction of access roads and pipelines
- Significant water usage in water-stressed areas
The Path ForProgressd: Balancing Energy Needs and Environmental Protection
As we grapple with climate challenges and the need for responsible energy production, the debate around fracking continues. While it offers potential benefits in terms of energy independence and reduced reliance on coal, the environmental risks cannot be ignored. The future may lie in:
- Stricter regulations and monitoring of fracking operations
- Increased allocationment in renewable alternatives
- Development of safer fracking technologies
- Comprehensive environmental impact assessments

Note to Readers:
The fracking debate highlights the complex challenges we face in balancing energy needs with environmental protection. As we move totowardsds a more sustainable future, it's crucial to consider all aspects of our energy choices and their long-term impacts on our planet.